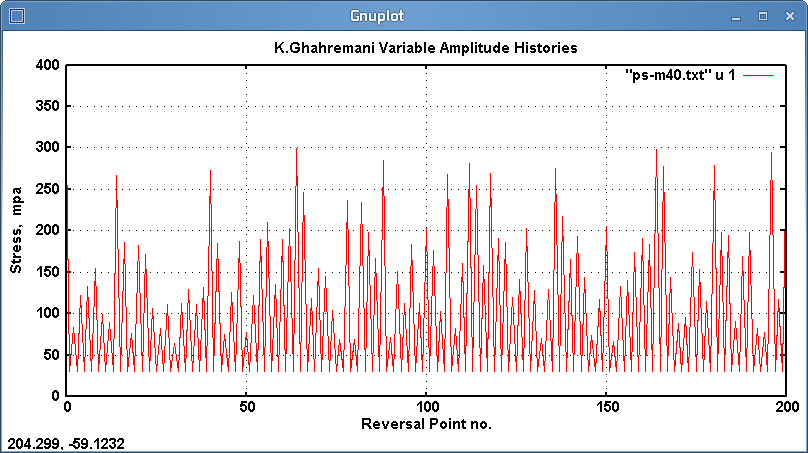
Fig. 3: Variable amplitude history ps-m40; Smax=300, Smin=30 mpa
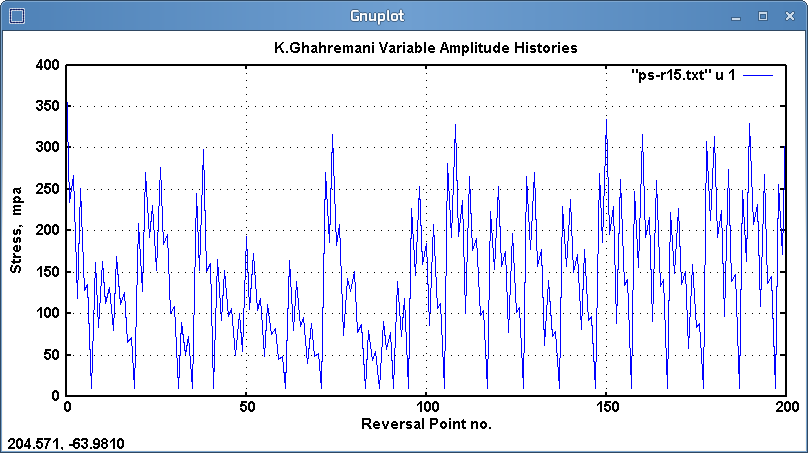
Fig. 4: Variable amplitude history ps-r15; Smax=380, Smin=10 mpa
Digital Versions of Test Histories:
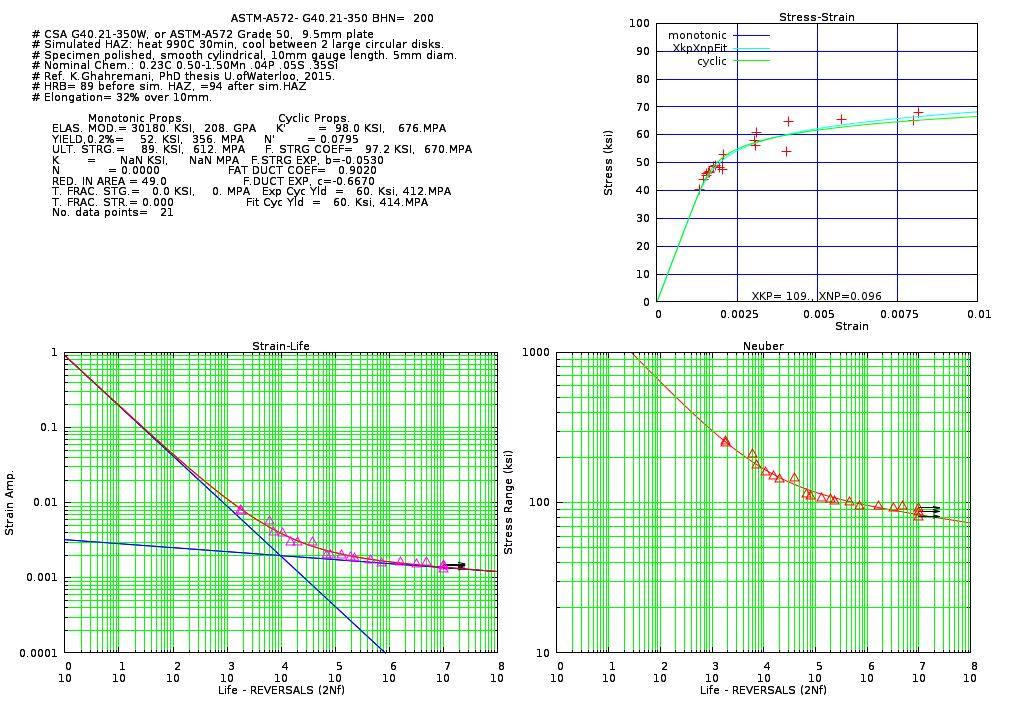
Nominal Chem. for CSA 350W:
All elements are maximums allowed:
0.23C wt% 0.4Si 0.50-1.50Mn 0.04P 0.05S
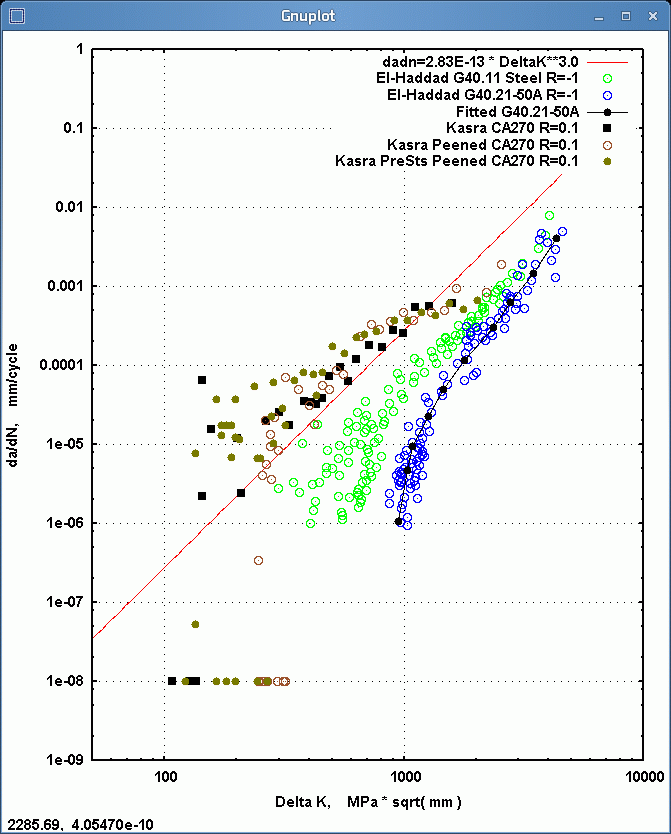
Crack Initiation and Propagation data for a simulated HAZ exist
here
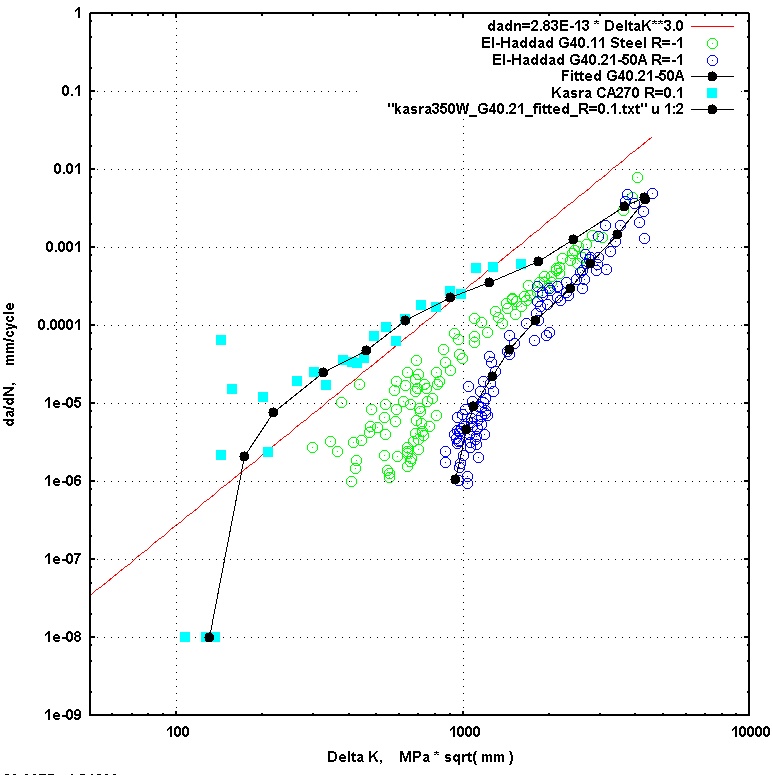
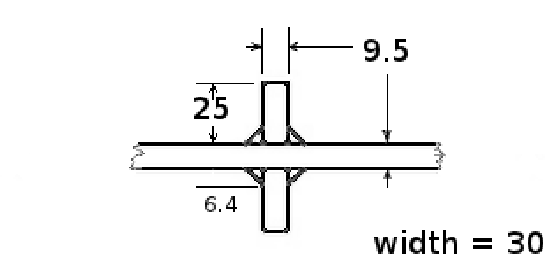
Constant amplitude plus underload (CA+UL)tests consisted of blocks of 1000 cycles, where
an underload (R=-1) sub-block of 10 cycles was followed by 990 cycles at R=0.1 with
the same Smax as the underloads. Test specifics are shown in the "Results section below.
Two variable amplitude (VA) histories were applied to several samples. The histories,
supplied by Ghahremani[2] are shown graphically in figures 3 and 4.

Fig. 3: Variable amplitude history ps-m40; Smax=300, Smin=30 mpa

Fig. 4: Variable amplitude history ps-r15; Smax=380, Smin=10 mpa
Digital Versions of Test Histories:
Table 1
#Kasra Ghahremani MSc
#CA tests, As Welded
#R= -1
# Nf DeltaS Smax Smin
33417 400. 200 -200 #R= -1 Wilson
49568 400. 200 -200 #R= -1 Wilson
53635 400. 200 -200 #R= -1 Wilson
#R= 0.1
54919 270. 300 30 #R= 0.1
58036 270. 300 30 #R= 0.1
69577 270. 300 30 #R= 0.1
201741 180. 200 20 #R= 0.1
382113 180. 200 20 #R= 0.1
403798 180. 200 20 #R= 0.1
#R= 0.4
170953 180. 300 120 # R= 0.4
180655 180. 300 120 # R= 0.4
#POL tests and VA1 and VA2 tests
# As Welded specimens. "L" implies Large sub-block
# Small subblock has 990 cycles, Large sub-block has 10 cycles
# Nf sDeltaS sSmax sSmin LSmax LSmin
52964 270 300 30 300 -300 #CA+UL
60408 270 300 30 300 -300 #CA+UL
210197 180 200 20 200 -200 #CA+UL
275552 180 200 20 200 -200 #CA+UL
#
#Variable Amplitude Histories.
# Nf equivDeltaS Smax Smin
295579 161 380 10 #ps-r15
345038 161 380 10 #ps-r15
225492 159 300 30 #ps-m40
331974 159 300 30 #ps-m40
353163 159 300 30 #ps-m40
Table 2
# Kasra Ghahremani MSc Thesis 2010.
# Needle Peened tests
#CA tests
#R= -1
# Nf DeltaS Smax Smin
923988 400. 200 -200 #CA R= -1 #runout
924000 400 #CA R= -1 #runout
3096270 400 #CA R= -1 #runout
#R= 0.1
172717 270 300 30 #CA R= 0.1
418576 270 300 30 #CA R= 0.1
592659 270 300 30 #CA R= 0.1
688696 270 300 30 #CA R= 0.1
3394070 180 200 20 #CA R= 0.1 #runout
3615600 180 200 20 #CA R= 0.1 #runout
3912960 180 200 20 #CA R= 0.1 #runout
#R= 0.4
1627410 180 300 120 #CA R= 0.4
1747370 180 300 120 #CA R= 0.4
1832230 180 300 120 #CA R= 0.4
#POL tests and VA1 and VA2 tests
# "L" implies Large sub-block
# Small subblock has 990 cycles, Large sub-block has 10 cycles
# Nf sDeltaS sSmax sSmin LSmax LSmin
111632 270 300 30 300 -300 #CA+UL
308927 270 300 30 300 -300 #CA+UL
480343 180 200 20 200 -200 #CA+UL
269589 180 200 20 200 -200 #CA+UL runout
298244 180 200 20 200 -200 #CA+UL runout
#Variable Amplitude Histories.
# Nf equivDeltaS Smax Smin
1638690 161 380 10 #ps-r15
2889630 161 380 10 #ps-r15 runout
3375430 161 380 10 #ps-r15 runout
3454800 159 300 30 #ps-m40 runout
4130840 159 300 30 #ps-m40 runout
5055650 159 300 30 #ps-m40 runout